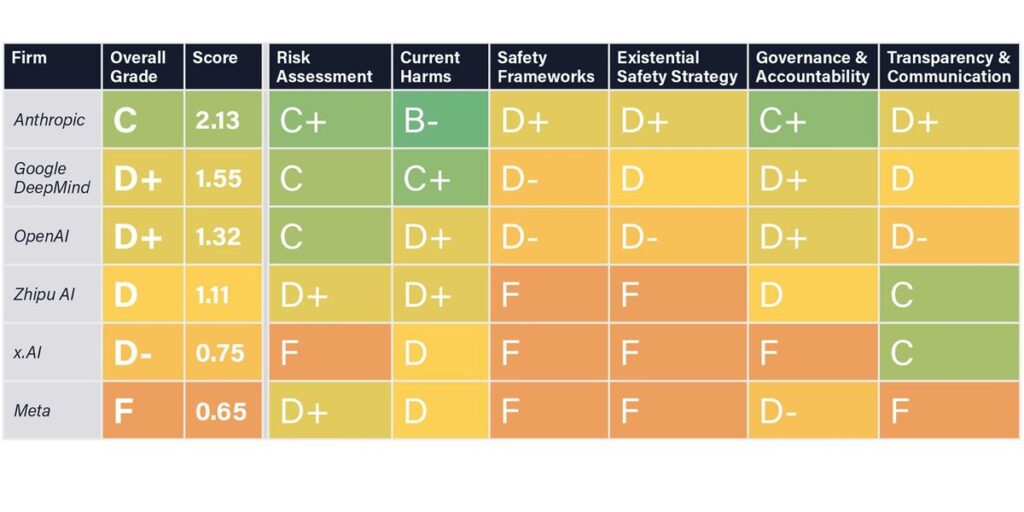
The just-released AI Safety Index graded six main AI corporations on their danger evaluation efforts and security procedures… and the highest of sophistication was Anthropic, with an general rating of C. The opposite 5 corporations—Google DeepMind, Meta, OpenAI, xAI, and Zhipu AI—obtained grades of D+ or decrease, with Meta flat out failing.
“The aim of this isn’t to disgrace anyone,” says Max Tegmark, an MIT physics professor and president of the Future of Life Institute, which put out the report. “It’s to offer incentives for corporations to enhance.” He hopes that firm executives will view the index like universities view the U.S. Information and World Experiences rankings: They could not take pleasure in being graded, but when the grades are on the market and getting consideration, they’ll really feel pushed to do higher subsequent yr.
He additionally hopes to assist researchers working in these corporations’ security groups. If an organization isn’t feeling exterior stress to fulfill security requirements, Tegmark says,“then different individuals within the firm will simply view you as a nuisance, somebody who’s attempting to sluggish issues down and throw gravel within the equipment.” But when these security researchers are abruptly accountable for bettering the corporate’s fame, they’ll get assets, respect, and affect.
The Way forward for Life Institute is a nonprofit devoted to serving to humanity beat back really dangerous outcomes from highly effective applied sciences, and lately it has centered on AI. In 2023, the group put out what got here to be referred to as “the pause letter,” which known as on AI labs to pause development of superior fashions for six months, and to make use of that point to develop security requirements. Huge names like Elon Musk and Steve Wozniak signed the letter (and up to now, a complete of 33,707 have signed), however the corporations didn’t pause.
This new report can also be ignored by the businesses in query. IEEE Spectrum reached out to all the businesses for remark, however solely Google DeepMind responded, offering the next assertion: “Whereas the index incorporates a few of Google DeepMind’s AI security efforts, and displays industry-adopted benchmarks, our complete method to AI security extends past what’s captured. We stay dedicated to repeatedly evolving our security measures alongside our technological developments.”
How the AI Security Index graded the businesses
The Index graded the businesses on how nicely they’re doing in six classes: danger evaluation, present harms, security frameworks, existential security technique, governance and accountability, and transparency and communication. It drew on publicly out there data, together with associated analysis papers, coverage paperwork, information articles, and {industry} stories. The reviewers additionally despatched a questionnaire to every firm, however solely xAI and the Chinese language firm Zhipu AI (which at present has essentially the most succesful Chinese language-language LLM) stuffed theirs out, boosting these two corporations’ scores for transparency.
The grades got by seven impartial reviewers, together with huge names like UC Berkeley professor Stuart Russell and Turing Award winner Yoshua Bengio, who’ve stated that superintelligent AI might pose an existential risk to humanity. The reviewers additionally included AI leaders who’ve centered on near-term harms of AI like algorithmic bias and poisonous language, corresponding to Carnegie Mellon College’s Atoosa Kasirzadeh and Sneha Revanur, the founding father of Encode Justice.
And general, the reviewers weren’t impressed. “The findings of the AI Security Index undertaking counsel that though there may be lots of exercise at AI corporations that goes beneath the heading of ‘security,’ it’s not but very efficient,” says Russell.“Particularly, none of the present exercise supplies any type of quantitative assure of security; nor does it appear doable to offer such ensures given the present method to AI through big black packing containers skilled on unimaginably huge portions of knowledge. And it’s solely going to get tougher as these AI techniques get larger. In different phrases, it’s doable that the present know-how path can by no means assist the mandatory security ensures, wherein case it’s actually a useless finish.”
Anthropic acquired the most effective scores general and the most effective particular rating, getting the one B- for its work on present harms. The report notes that Anthropic’s fashions have obtained the very best scores on main security benchmarks. The corporate additionally has a “responsible scaling policy“ mandating that the corporate will assess its fashions for his or her potential to trigger catastrophic harms, and won’t deploy fashions that the corporate judges too dangerous.
All six corporations scaled notably badly on their existential safety methods. The reviewers famous that all the corporations have declared their intention to construct artificial general intelligence (AGI), however solely Anthropic, Google DeepMind, and OpenAI have articulated any type of technique for making certain that the AGI stays aligned with human values. “The reality is, no person is aware of how one can management a brand new species that’s a lot smarter than us,” Tegmark says. “The assessment panel felt that even the [companies] that had some kind of early-stage methods, they weren’t enough.”
Whereas the report doesn’t challenge any suggestions for both AI corporations or policymakers, Tegmark feels strongly that its findings present a transparent want for regulatory oversight—a authorities entity equal to the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration that may approve AI merchandise earlier than they attain the market.
“I really feel that the leaders of those corporations are trapped in a race to the underside that none of them can get out of, irrespective of how kind-hearted they’re,” Tegmark says. In the present day, he says, corporations are unwilling to decelerate for security checks as a result of they don’t need rivals to beat them to the market. “Whereas if there are security requirements, then as a substitute there’s business stress to see who can meet the protection requirements first, as a result of then they get to promote first and earn money first.”
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet