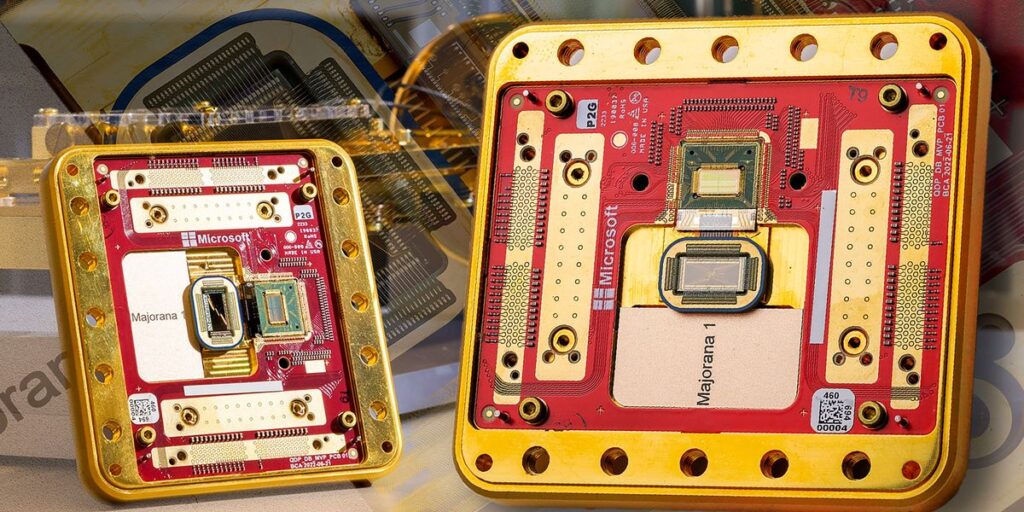
Yesterday, three members of Microsoft’s quantum crew presented their work in the direction of a topological quantum computer on the APS Global Summit in Anaheim. Final month, the crew made waves announcing their first topological quantum chip, the Majorana 1. Extra quietly, Nokia Bell Labs has been working on their very own model of a topological quantum laptop, and the corporate claims it’s demonstrated the important thing components in 2023. Each efforts symbolize scientific achievements, however bulletproof proof of a topological quantum bit is elusive.
“I’d say all quantum computing is early levels,” says Bertrand Halperin, emeritus professor of physics at Harvard, who isn’t concerned in both effort. “However topological quantum computing is additional behind. It may catch up; it’s taking a considerably totally different path.”
What’s a Topological Quantum Pc?
Quantum computers run on qubits valued at 0, 1, or some superposition of the 2, often encoded by way of some native quantum property—say, whether or not an electron’s spin is up or down. This provides quantum computer systems totally different capabilities than their classical cousins, promising to simply crack sure kinds of issues which are out of attain of even the most important supercomputers. The problem is that these quantum superpositions are very fragile. Any noise within the surroundings, be it temperature fluctuations or small adjustments in electrical or magnetic fields, can knock qubits out of superposition, inflicting errors.
Topological quantum computing is a essentially totally different method to constructing a qubit, one which in concept could be a a lot much less fragile. The thought is that as a substitute of utilizing some native property to encode the qubit, you’d use a worldwide, topological property of an entire sea of electrons. Topology is a subject of mathematics that offers with shapes: Two shapes are topologically similar if they are often remodeled into one another with out tearing new holes or connecting beforehand unconnected ends. For instance, an infinite rope extending into area is topologically distinct from the identical rope with a knot in it.
Electrons can “twist” round one another to kind one thing akin to a knot. This knot is harder to tie or untie, providing safety in opposition to noise. (That is an analogy—the qubits wouldn’t be literal knots. For a full technical rationalization, see this “short” introduction.)
The problem is that electrons don’t usually naturally twist themselves into knots. Theorists have postulated such states may existfor many years, however creating the proper circumstances for them to come up in observe has been elusive. It’s extraordinarily troublesome to make units that might give rise to knotted electrons, and arguably much more troublesome to show that one has performed so.
Microsoft’s “Quantraversy”
The Microsoft crew’s method to creating knotted electrons is to begin with a semiconducting nanowire. Then, they layer a superconducting materials on high of this nanowire. Each the semiconductor and superconductor layers should be virtually utterly devoid of fabric defects, and held at millikelvin temperatures. In concept, this enables an electron from the semiconducting layer to make use of the superconductor to successfully unfold out over the entire wire, forming one thing akin to a rope that may be tied into knots. This rope is known as a Majorana zero mode.
Definitively displaying that they’ve created a Majorana zero mode has confirmed troublesome for the Microsoft crew. The crew and their collaborators claimed that they had achieved this milestone again in 2018, however some researchers had been unconvinced by the proof, saying imperfections within the system may have resulted in the identical measurements. The paper bought retracted. In 2023, Microsoft and collaborators published additional proof that they’ve created Majoranas, though some scientists have remained unconvinced, and say not sufficient information was shared to breed the outcomes. Final month’s claim remains contentious.
“We’re very assured that our units host Majorana zero modes,” says Chetan Nayak, the lead of the Microsoft effort.
“There isn’t a proof of even the essential physics of Majoranas in these units, not to mention that you would construct a qubit out of them,” says Henry Legg, lecturer on the College of St. Andrews who has authored two preprints disputing Microsoft’s outcomes.
“We might in all probability all agree that additional experiments and higher information are essential earlier than the difficulty will be thought-about closed,” Harvard’s Halperin says.
Whether or not or not the Microsoft crew has created Majorana zero modes, making them is simply step one. The crew additionally has to point out they are often manipulated to really do computations. A number of kinds of operations are required to make the type of knot that represents 0, untie it and tie it right into a knot that represents 1, or create a quantum superposition of the 2.
The latest paper demonstrated the crew’s functionality to do one of many essential measurements. “It’s a giant step,” says Jay Sau, professor of physics on the College of Maryland who has a consulting appointment with the Microsoft crew.
In an uncommon transfer, Microsoft’s quantum crew held a restricted entry assembly at their headquarters at Station Q, and invited a number of researchers within the subject. There, they revealed preliminary outcomes demonstrating one other such measurement.
“There’s nonetheless fairly a bit of labor to do on that aspect,” says Michael Eggleston, information and units chief at Nokia, who was current on the Station Q assembly. “There’s a variety of noise in that system. However I feel they’re on path.”
To sum up, the Microsoft crew has not but reached the milestone the place the scientific group would agree that they’ve created a single topological qubit.
“They’ve an idea chip which has eight lithographically fabricated qubits,” Eggleston says. “However they’re not useful qubits, that’s the advantageous print. It’s their idea of what they’re transferring in the direction of.”
Nokia Bell Labs quantum computing researchers Hasan Siddiquee (proper) and Ian Crawley connecting a dilution fridge pattern loader for cooldown.Nokia Bell Labs
Nokia’s Method
A crew at Nokia Bell Labs can be pursuing the dream of topological quantum computers, though by way of a distinct bodily implementation. The crew, led by lifelong topological quantum computing devotee Robert Willet, is sandwiching a skinny sheet of gallium arsenide in between two different semiconducting slabs. They then cool the sandwich to millikelvin temperaturesand topic it to a powerful magnetic subject. If the system properties are good, this might give rise to a two-dimensional model of a worldwide digital state that may be tangled up. A qubit would require each the creation of this state, and the power to controllably knot and unknot it.
Robert Willet and his collaborators have additionally had bother convincing the scientific group that what that they had on their arms are actually the extremely coveted topological states.
“We’re very assured that we’ve got a topological state,” says Nokia’s Eggleston, who oversees the quantum computing effort.
“I discover it moderately convincing,” Harvard’s Halperin says. “However not everybody would agree.”
The Nokia crew has not but claimed the power to do operations with the system. Eggleston says they’re engaged on demonstrating these operations, and plan to have leads to the second quarter of this yr.
Proving Topological Quantum States
Proving the mandatory topological components past the shadow of a doubt stays elusive. Virtually talking, crucial factor isn’t whether or not the unique topological state will be confirmed to be current, however whether or not researchers can construct a qubit that’s each controllable and rather more strong in opposition to noise than approaches which are extra mature.
Nokia’s crew claims that they will keep error-free quantum superpositions for days, though they can’t management them but. Information revealed by Microsoft on the Station Q assembly reveals their units stay error-free for 5 microseconds, however they consider this may be improved. (For comparability, a convention superconducting qubit in IBM’s quantum laptop stays error-free for as much as 400 microseconds).
“There’s all the time going to be individuals who don’t essentially agree or need extra information,” Nokia’s Egglestein says, “and I feel that’s the energy of the scientific group to all the time ask for extra. Our feeling on that is you’ll want to scale up complexity of units.”
“I feel in some unspecified time in the future you go to the regime the place it’s a fairly good qubit, whether or not it’s exactly topological or not, that turns into the purpose of the controversy,” Maryland’s Sau says. “However at that time it’s extra helpful to ask how good or dangerous of a qubit it’s.”
Regardless of difficulties, topological quantum computing continues to be—at the least theoretically—a really promising method.
“I have a look at these different qubit varieties that we see on the market at this time. They’re very nice demonstrations. It’s nice science. It’s actually arduous engineering. Sadly, it’s type of just like the vacuum tube again within the 40s,” Egglestein says. “You construct computer systems out of them as a result of that’s all you’ve, they usually’re actually difficult to scale up. To me, topological qubits actually supply the potential that the transistor did. One thing small, one thing strong, one thing that’s scalable. And that’s what I feel the way forward for quantum computing is.”
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet