Most haptic interfaces at the moment are restricted to easy vibrations. Whereas visible shows and audio programs have continued to progress, these utilizing our sense of contact have largely stagnated. Now, researchers have developed a haptics system that creates extra complicated tactile feedback. Past simply buzzing, the machine simulates sensations like pinching, stretching, and tapping for a extra lifelike expertise.
“The feeling of contact is probably the most private connection you could have with one other particular person,” says John Rogers, a professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, who led the venture. “It’s actually vital, however it’s far more troublesome than audio or video.”
Co-led by Rogers and Yonggang Huang, additionally a professor at Northwestern, the work is essentially geared towards medical functions. However the know-how could possibly be utilized in a variety of functions, together with virtual or augmented reality and feeling the feel of clothes material or different objects whereas procuring on-line. The analysis was published within the journal Science on 27 March.
A Nuanced Sense of Contact
As we speak’s haptic interfaces principally depend on vibrating actuators, that are pretty easy to assemble. “It’s an ideal place to start out,” says Rogers. However going past vibration might assist add the vibrancy of real-world interactions to the know-how, he provides.
A lot of these interactions require extra subtle mechanical forces, which embody a mix of each regular forces directed perpendicular to the pores and skin’s floor and shear forces directed parallel. Whether or not by way of vibration or making use of stress, forces directed vertically into the pores and skin have been the primary focus of haptic designs, in response to Rogers. However these don’t absolutely have interaction the numerous receptors embedded in our pores and skin.
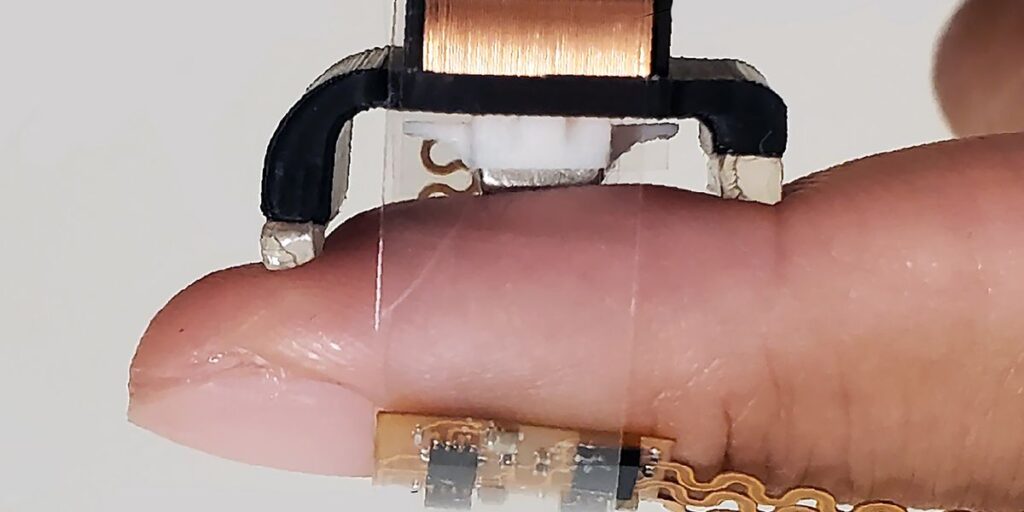
The researchers aimed to construct an actuator that gives full freedom of movement, which they achieved with “very outdated physics,” Rogers says—specifically, electromagnetism. The essential design of the machine consists of three nested copper coils and a small magnet. Working present by way of the coils generates a magnetic area that then strikes the magnet, which delivers pressure to the pores and skin.
“What we’ve put collectively is an engineering embodiment [of the physics] that gives a really compact pressure supply system and provides full programmability in course, amplitude, and temporal traits,” says Rogers. For a extra elaborate setup, the researchers additionally developed a model that makes use of a set of 4 magnets with completely different orientations of north and south poles. This creates much more complicated sensations of pinching, stretching, and twisting.
Haptics at Your Fingertips—Or Anyplace
As a result of fingertips are extremely delicate, solely small forces are wanted for this utility. John A. Rogers/Northwestern College
Though a lot of the earlier work in haptics has targeted on fingertips and the fingers, these gadgets could possibly be positioned elsewhere on the physique, together with the again, chest, or arms. Nevertheless, these functions might have completely different necessities. In comparison with locations just like the again, the fingertips are extremely delicate—each by way of the pressure wanted and the spatial density of receptors.
“The fingertips are most likely probably the most difficult by way of density, however they’re best by way of the forces that you’ll want to ship,” says Rogers. In different use circumstances, delivering sufficient energy could also be a problem, he acknowledges.
The pressure potential can also be restricted by the dimensions of the coils, says Gregory Gerling, a systems engineering professor on the College of Virginia and former chair of the IEEE Technical Committee on Haptics. The coil dimension dictates how a lot pressure you may generate, and at a sure level, the machine received’t be wearable. Nevertheless, he believes it’s ample for VR functions.
Gerling, an IEEE senior member, finds using magnetism in a number of instructions fascinating. In comparison with different approaches which are primarily based on hydraulics or air stress, this method doesn’t require pumping fluids or gasses. “You might be form of untethered,” Gerling says. “Total, it’s a really fascinating, novel machine, and perhaps it takes the sphere in a barely new course.”
Purposes in VR, Neuropathy, and Extra
The clearest utility of the machine might be in digital or augmented reality, says Rogers. These environments now have extremely subtle audio and video inputs, “however the tactile part of that have remains to be a piece in progress,” he says.
Their lab, nevertheless, is primarily targeted on medical functions, together with sensory substitution for sufferers who’ve misplaced sensation in part of the physique. A posh haptics interface might reproduce the feeling in one other a part of the physique.
For instance, nerve injury in individuals with diabetic neuropathy makes it troublesome for them to stroll with out their toes. The lab is experimenting with putting an array of pressure sensors into the bottom of those sufferers’ footwear, then reproducing the sample of stress utilizing a haptic array mounted on their higher thighs, the place they nonetheless have sensation. The researchers are working with a rehabilitation facility in Chicago to check the strategy, primarily with this inhabitants.
Persevering with to develop these medical functions will probably be a spotlight shifting ahead, says Rogers. When it comes to engineering, he want to additional miniaturize the actuators to make dense arrays potential in areas of the physique just like the fingertips.
Feeling the Music
Moreover, the researchers explored the potential of utilizing the machine to extend engagement in musical performances. Other than maybe feeling vibrations of the bass line, performances often depend on sight and sound. Including a tactile ingredient might make for a extra immersive expertise, or assist individuals with hearing impairment have interaction with the music.
With the present tech, fundamental vibrating actuators can change the frequency of vibration to match the notes being performed. Whereas this will convey a easy melody, it lacks the richness of various devices and musical elements.
The researchers’ full freedom of movement actuator can convey a extra vibrant sound. Voice, guitar, and drums, as an illustration, can every be transformed into a selected pressure supply mechanism. Like with vibration alone, the frequency of every pressure might be modulated to match the music. The experiment was exploratory, Rogers says, however exploits the superior capabilities of the system.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net